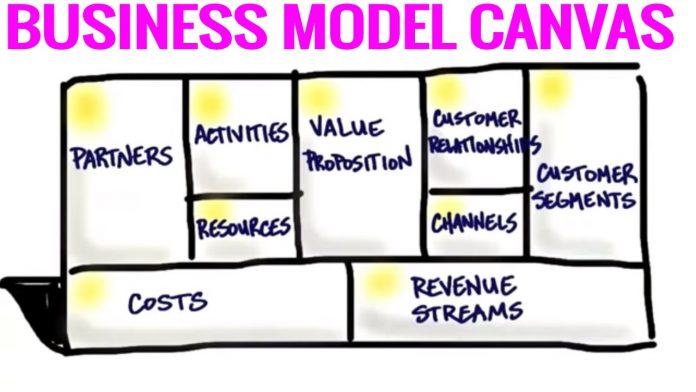
Canvas Business Model is an organizational chart and lean startup strategy template for creating new or documenting existing businesses. It is basically a graphical chart with basic components describing the key characteristics of a product or company. The key characteristic to focus on in a diagrammatic representation of the business model is the main function of the organization.
This main function is usually represented as the axis on which the diagram is drawn. The other main factors to be considered are the relationship between this axis and all other axis. The relationship between axes can also be represented as a line between each axis. This concept is similar to the horizontal axis of a table. As a result, the diagram may also be represented by two horizontal lines. This will help you better visualize your product and/or business model in a graphical format.
Canvas Business Model is Effective Approach
Canvas Business Model allows for a more efficient approach in developing strategies. A diagrammatic representation of the strategy may also include an operational definition. This operational definition may be represented by a diagrammatic depiction of a specific phase of the business model. Some of these phases include the discovery of product, pricing model, distribution, and marketing. A diagrammatic representation of the strategy in a Canvas Business Model will show the overall strategy and its related activities in graphical form. This can be helpful to present a business model to managers in a very clear manner. For example, the strategy of a company may be represented as a series of steps or stages of actions taken to bring about the success of the business model.
Another aspect that should be incorporated in Canvas Business Model is the measurement of progress made towards the end goal of the strategy. You can use the diagrammatic representation to create an outline of the success of the strategy and how the strategy is progressing. This will provide managers with an overview of the strategy. They can then create an action plan for moving the company towards the success of the strategy.
Lean manufacturing, in particular, has been known to provide a comprehensive tool to the business and the managers. The diagrammatic representation helps to define the scope, design, and test the tools that will be used during lean manufacturing. in a proper way. The diagrammatic presentation of the tools is necessary to create an efficient and cost effective system for Lean manufacturing. The graphically described tools canvas business model can be used for testing, development, testing, and evaluating the software, process, and hardware used in the production cycle. It helps in measuring both process and results.
A Canvas Business Model can also be used to show the status of a company in terms of capital and time. The map represents the business and shows the amount of money required to start up the business. it also helps in determining the costs of capital and labor. The map can also show the percentage of sales that are made through overhead and profits. This graph shows the percentage of sales made through gross and net, respectively.
1. Business Model Canvas Introduction
It is a business model Canvas created by Professor Yves Pigneur of the University of Lausanne in Switzerland and his student Alexander Osterwalder. It is a business model framework that contains the core components of the business model on a single canvas and diagrams the process of creating customer value. There is a characteristic that it can be.
Alexander Osterwalder and Yes Pignoer, the creators of the business model canvas, defined business models in their first co-book, “Business Model Generation,” as follows:
“A business model Canvas is a rational and systematic description of how an organization creates, disseminates, and captures value.”
To understand the principles of how companies create and disseminate customer value, and how they generate revenue, it is necessary to understand the nine building blocks, which are the nine components that make up the business model canvas. to be. The nine elements of the business model canvas are customers, value propositions, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, core resources, core activities, core partners, and costs.These are the four key areas of business: customer, order, infrastructure, business feasibility analysis, etc. It is explained that it encompasses.
It is widely used in education/workshops, etc. for the advantage of being able to express business items that remain only as simple ideas in a business model by filling nine blanks in a single canvas. There are many templates that help organize models/concepts, etc. into a single canvas.
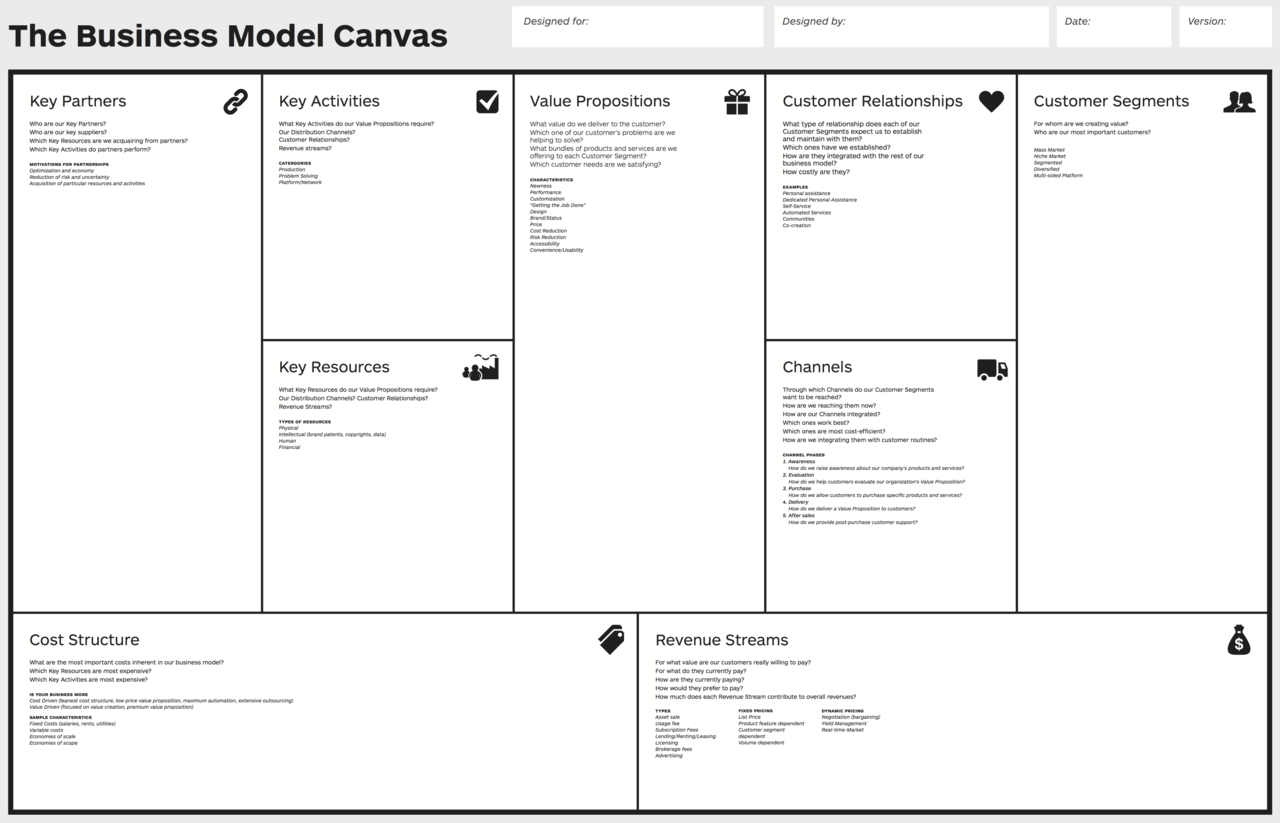
2. How to use the Business Canvas Model
Business model canvas is simple. All you have to do is to organize and fill in the contents of your business items for the nine elements in the canvas. In order to use this framework effectively, you must first clearly understand what the nine elements in the business model canvas mean and what should be written.
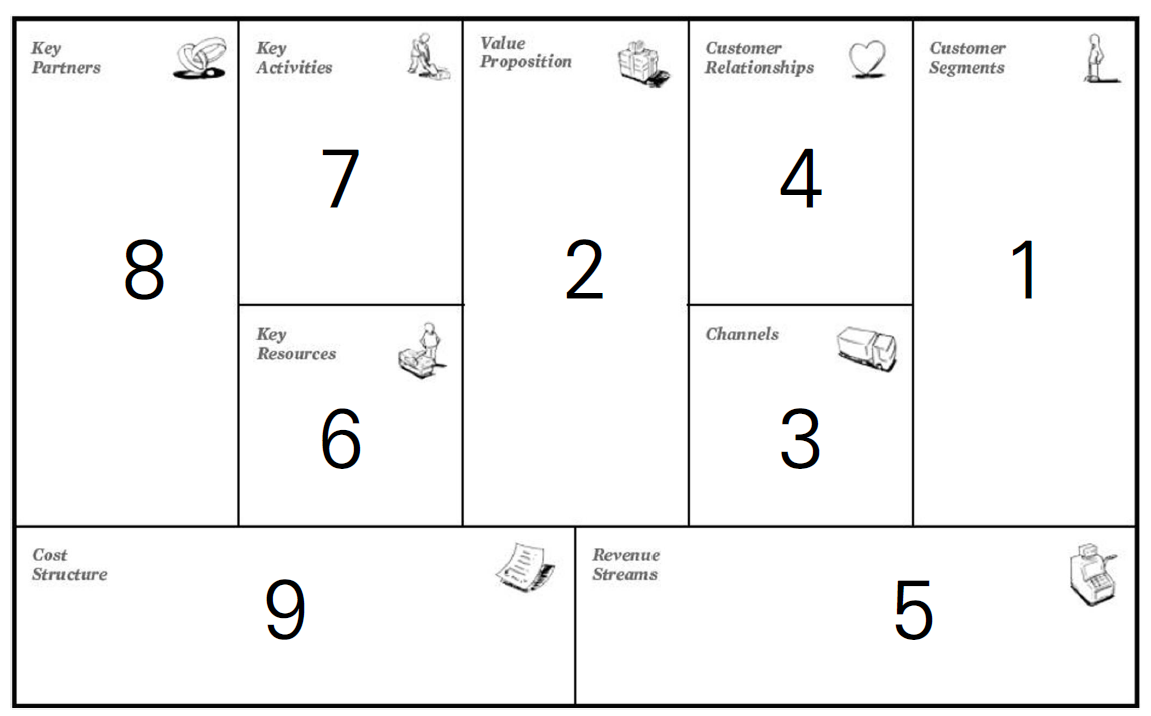
Description of 9 Business Model Canvas components
1) Customer Segment
Defines who our target customer group is and what problems/concerns/needs we have. A customer segment is not simply referring to each individual customer, but rather as a group of customers that have a certain commonality. The common point mentioned here is anything that can be expressed in a specific standard, such as using a specific distribution channel, thinking more seriously about a specific problem/task/needs, or living in a specific area.
There are different types of customer segments, some of which are mass markets, niche markets, well-segmented markets, mixed-segment markets, and multisided markets (e.g. marketplaces, platforms, etc.).
An organization provides a product or service to one or more customer segments.
It specifies how different types of people or organizations each company targets. Depending on what the business model (BM) is, the customer segment can be one or divided into several. You also have to decide which segments to target as key targets and which segments you don’t need to focus on. The segmentation can be clarified by dividing the customer based on the following criteria.
- The customer needs a completely different service or product.
- The distribution channels that approach the customer are different.
- It requires a completely different type of customer relationship.
- There are significant differences in profitability.
- They are willing to pay for other types of products.
The Strength of Business Relationships: The Key To Business Contracts
2) Value Proposition
Refers to a combination of products or services to create the value required by a specific customer segment. When organizing a value proposition, rather than simply covering all the products or services we provide, we define a’sharp something’ that can only differentiate ourselves to solve the biggest problems/needs of our target customer segment as defined above. It is necessary to organize. Listed below are the factors that a specific customer segment can consider as value. -Newness, performance, customization, making things happen, design, brand status, price, cost reduction, risk reduction, accessibility, convenience/usefulness, etc.It is necessary to define and organize’something sharp’ that only us can differentially solve the biggest problems/needs of our target customer segment as defined above.
When defining a value proposition with the above value elements, it is important to note that it is not expressed in terms of fast speed and low price, but above all, the target customer segment has been used to solve their needs. The definition of how much more valuable it is compared to the alternative (competitive or substitute) used is to write it with a much higher understanding.
Organizations provide specific values that solve their problems and satisfy their needs.
A combination of products or services to create the value required by a specific customer segment. “Value” is the element that satisfies the customer’s thirst or meets their needs. Therefore, clear elements that meet the needs of the segment must be combined. Such factors include:
- newness
- performance
- customizing
- Making something ‘being’: Just by helping customers do something, the value can be created Rolls-Royce, for example, manufactures and supplies jet engines owned by airline customers, as well as overhauls.
- design
- Brand status
- price
- cut down the money
- Risk reduction
- accessibility
- Convenience/Usability
3) Channels Channel
Refers to all methods of communicating with target customer segments and transacting products/services. When considering channels, most are’Where do customers buy our products/services?’ There is a tendency to focus only on the part and think about it, but in fact, in order to think about the real customer channel and establish a strategy, it is necessary to cover both the steps before and after the purchase.
In the book, there are five elements of customer channel:’understanding-evaluation-purchase-delivery-after-sales’, and it is necessary to consider how to communicate with customers for each individual element.
* Understanding: How will you improve your customers’ understanding of your product or service?
* Evaluation: How will you help your customers properly evaluate the value proposition?
* Purchasing: How can you make your customers purchase products or services more smoothly?
* Delivery: How will you deliver the value proposition to your customers?
* After sale: How to support purchasing customers?
This is not much different from problem recognition-information search-alternative evaluation-purchase decision-post-purchase action’, which is a general customer’s purchase decision-making process.
The value provided by the organization reaches customers through communication, logistics, and sales channels.
It refers to the way a business communicates and delivers a product or service to offer value to a customer segment. The channel performs the following functions.
- It enhances customers’ understanding of the products or services provided by the company.
- It allows customers to evaluate the value proposition delivered by the company.
- Helps customers purchase specific products or services.
- Deliver value proposition to customers.
- Provides After Service (AS) for purchasing customers.
The following are the elements that make up the channel.
- Understanding: How will you improve your customers’ understanding of your product or service?
- Evaluation: How will you help your customers properly evaluate the value proposition?
- Purchasing: How can you make it easier for customers to purchase goods or services?
- Delivery: How to deliver the value proposition to the customer?
- After sale: how to support purchasing customers?
In summary, in order to create a channel block, it is necessary to consider not only the vendor but also the purchase process before and after.
4) Customer Relationships
This refers to the type of relationship to be established with a specific customer segment. Having a relationship with a customer is easy to understand as making a first-time visitor a member of our site, a member of our site as a buyer of our product/service, and a repeater who repeatedly purchases our product/service. And the ultimate goal of building customer relationships is to turn customers into’fans’ of our brand.
For consumers who visit us once or purchase goods/services to become our fans, the customer experience (UX) we provide to our customers must be superior to other alternatives. To this end, the entire process, when a customer experiences us to solve a problem or meet a need, must be designed to exceed its purpose.
The book explains some of the common ways of forming customer relationships with specific customer segments.
* Individual assistance (eg: call center, email customer center, etc.)
* Very dedicated individual assistance (eg: private banking service, dedicated driver service, etc.)
* Self-service (eg kiosk, FAQ page, etc.)
* Automation service (e.g., customized curation service based on customer data)
* Community (e.g. Microsoft Tech Community, Nike Mania, Used Nara, etc.)
* Co-creation (e.g. YouTube-Customers’ own comments, Ratings, furthermore, content consumption such as activities as creators, and production at the same time)
Relationships with customers are established and maintained characteristically for each customer segment.
It means what kind of relationship you will have with a specific customer segment. The reasons for maintaining customer relationships include’customer acquisition’,’customer retention’, and’sales promotion’. Examples of customer relationship formation are as follows.
- Individual assist
- Very dedicated individual assist
- Self-service
- Automation service
- community
- Co-Creation: Inducing customers to create content themselves like YouTube
5) Revenue Streams
Revenue Streams Refers to cash generated from customer segments. Define the revenue stream of how and how much money we get for the value proposition we provide to solve the problem/needs of our customer segment.
It is necessary to establish a specific business model not simply to define the types of revenue sources, but to consider specific prices (or commission rates) for each revenue source.
Organizations earn money when they successfully deliver the value they want to deliver to their customers.
Revenue source refers to the cash a company generates from each customer segment (revenue-cost=revenue). In the broader framework, there are two sources of revenue:’revenue derived from one-time expenditure of customers’ and’repetitive revenue generated from consecutive expenditures of delivering self-government proposals to customers or supporting customers after purchase’. The following is an example of revenue source
- Sell goods
- Usage fee
- Subscription fee
- Rental fee/rent fee
- Licensing
- Brokerage Fee
- Advertising
6) Key Resources Core
These Core Resources are the most important assets needed to run our business smoothly. In the book, core resources are largely classified into four categories:
* Physical resources
* Intellectual assets
* Human resources
* Financial resources
7) Key Activities Core Activities
Our core value proposition requires consideration of which core activities are required. In the book, it is largely classified into three categories:
* Production
* Problem solving
* Platform/Network
8) Key Partnerships
A network between suppliers and partners that can smoothly operate the core partnership business model.
Partnership types can be classified into four broad categories:
* Strategic alliance among non-competitors
* Strategic partnership among competitors (Coopetition)
* Joint venture to develop new business
*’Buyer-supplier’ relationship to secure stable supply
9) Cost Structure
This refers to all costs incurred in operating the business model. The cost structure is largely divided into fixed cost and variable cost, and it is necessary to consider the item and size of the cost for each cost.
A story about how to make money by creating and providing customer value is completed just by arranging blocks 1 to 9 of the business model canvas in order. This story works as a story plot that can explain my business items more concisely and intuitively than any other plot.
As such, the main reason for using the business model canvas is that it is possible to unify the concept of business items scattered in the head by meticulously thinking about this single canvas that seems simple. Of course, there are criticisms that there is no consideration of the market environment or the competitive environment in the process of arranging business models, but it is an excellent tool for organizing business ideas at the level of business models in a short time, especially when thinking as a team rather than alone. It is a framework that helps to align the thinking/understanding of the team members’ business models, and it can be said to be a framework that has many advantages over disadvantages.
Strategyzer, a business modeling solution/workshop/consulting company founded by Alexander Osterwalder, the creator of BMC, uses BMC to 1) visualize existing businesses simply 2) design new business models in existing business areas or in new markets. , 3) It is proposed that it can be used as a tool to manage various business portfolios within the company.
As such, BMC is not simply used as a tool to materialize business items, but a framework that can be used in various ways such as analyzing existing business models (including competitors), managing business models, and sharing business ideas among stakeholders.
Business Model Canvas
During the new employee training period, the task of planning a new business with the company’s products and writing a business plan was given to understand the business overall. Therefore, I also took a lecture related to the business model canvas, but I wrote it so long ago that I can’t remember it, so I want to organize it a little.
What is Business Model Canvas?
A business model is a logical description of how an organization captures, creates, and disseminates value . And the business model canvas is a diagram of the nine main business elements that must be included in the business.